Hong Kong buildings account for the majority of city-wide electricity consumption and carbon emissions – over 90% and 60% respectively. Over the years, we have spared no effort to adopt innovative sustainable and smart building designs which efficiently use energy, materials and land resources.
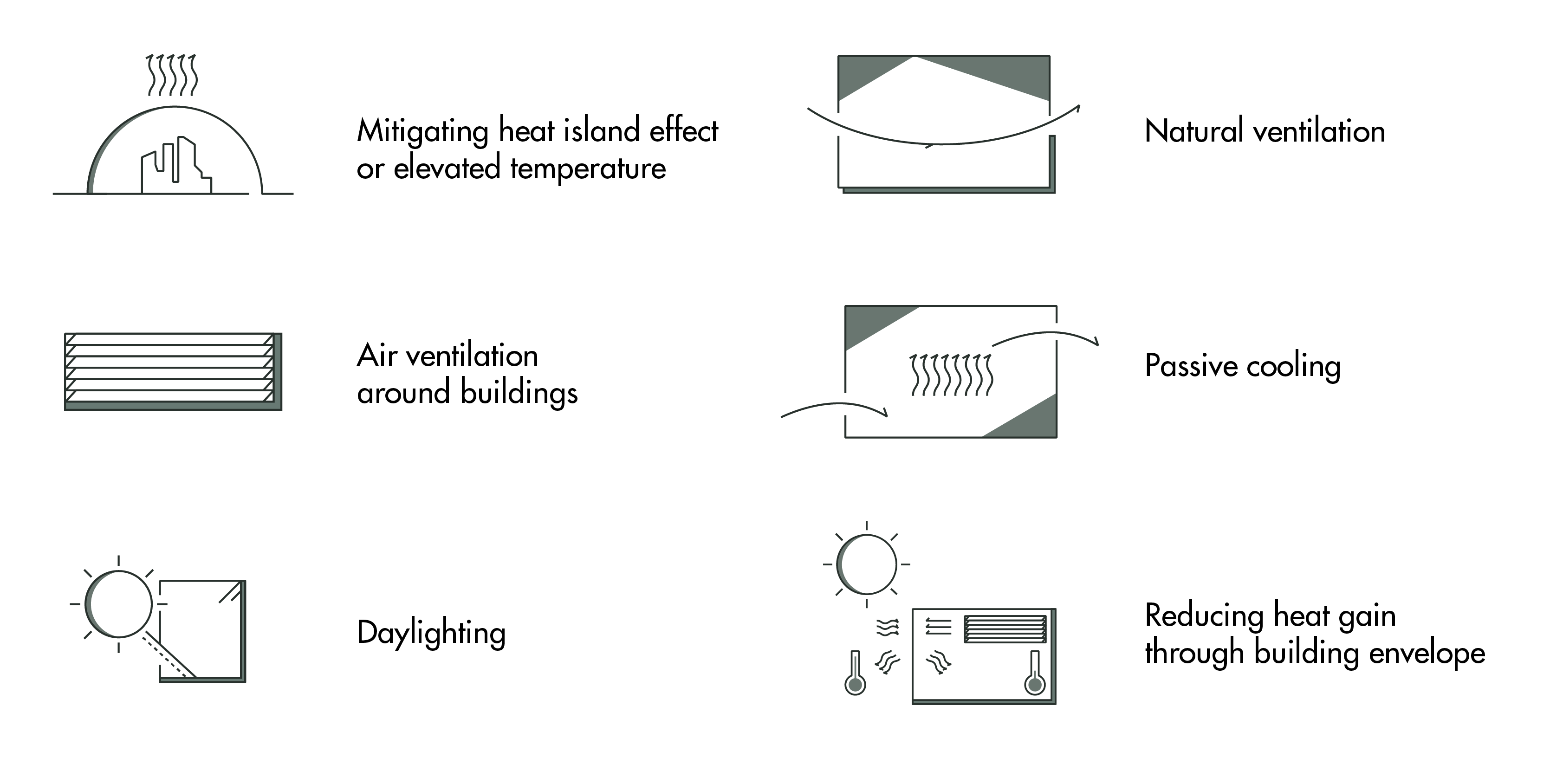
Passive design approaches use the architecture of a building to minimise energy consumption and improve thermal comfort. These approaches adopt suitable planning, disposition, orientation, building form and material selection measures to optimise a building's interaction with the local microclimate. The aspects considered include:
Building Information Modelling, or BIM, technology is essentially the process of generating a digital visual representation of building data. BIM can effectively improve overall building quality through design optimisation, communication enhancement and waste minimisation. For example, BIM allows the visualisation of designs that enhance the planning process; they can also simulate the entire construction process to facilitate more efficient coordination between stakeholders. The technology has contributed to a significant reduction in aborted works caused by unworkable designs and safety pitfalls.
During the reporting year, ArchSD used BIM on several projects. One of these projects was the construction of West Kowloon Government Offices, for which BIM was used to enhance project efficiency.
Modular Integrated Construction (MiC) is a catch-all term for an important concept: factory assembly followed by on-site installation. MiC is one example of Design for Manufacture and Assembly (DfMA), which refers to a construction method that uses free-standing volumetric modules with completed finishes, fixtures and fittings. This construction method transfers traditional on-site construction processes to an off-site prefabrication factory; something which can substantially improve construction productivity by minimising site constraints and ensuring a higher degree of quality control. During the year, ArchSD commenced the first pilot public building project to adopt MiC in Hong Kong - The Construction of Disciplined Services Quarters for the Fire Services Department at Pak Shing Kok in Tseung Kwan O.
Another important aspect of sustainable buildings is the selection and use of sustainable construction methods and materials. Common practices include prefabrication, pollution control during construction, and the application of the 3R principles – reduce, reuse and recycle – to manage construction and demolition waste. In terms of using sustainable materials, recycled materials and timber from well-managed sources are widely adopted in ArchSD's new building projects.
As a cosmopolitan city, Hong Kong places a high value on the accessibility and quality of public spaces. ArchSD strives to incorporate social considerations into our buildings in a number of ways, including enabling group activities and fostering communication between community members in order to create and sustain a harmonious atmosphere for the city.
The existing Hong Kong Museum of Art (HKMA) has been serving the public since 1991. To address a long-standing problem of a shortage of art exhibition space and to enhance the overall visitor experience, an expansion and renovation project is being carried out to upgrade the museum's facilities. The existing building volume is being preserved and redecorated to emphasise its symbolic value as a public museum belonging to all inhabitants of the city. Meanwhile, new cladding provides tangible texture that is reminiscent of a Chinese masonry pattern, while the façade's 'ripple effect' echoes the wave patterns of the waters of the adjacent Victoria Harbour.
The Policy Innovation and Co-ordination Office (PICO) commenced operation in 2018. The aim of PICO is to enhance policy innovation through collaboration on evidence-based policy research, support the senior leadership in the Government to focus on Hong Kong's strategic positioning in the global economic arena, co-ordinate major policies and programmes across bureaux and departments, and provide 'first-stop and one-stop' project consultation and co-ordination services to innovative projects to help maximise benefits to society. To improve the office design and enhance operational efficiency, a comprehensive renovation project was completed at PICO, located on the 26/F of the Central Government Offices at Tamar. The project included renovating the reception area, co-working area and open plan office.
Covering a total area of 15.8 hectares, Morse Park in Wong Tai Sin includes the Morse Park Sports Centre and Morse Park Swimming Pool. Serving the community since 1967, the park facilities have been continuously improved and upgraded over the years, with new facilities added to maintain an excellent standard of service and meet the emerging needs of the public. This project, conducted during the reporting year, is typical of these upgrades – enhancing the park's amphitheatre, including extending the cover at the stage and spectator areas, enlarging the stage area and rearranging the spectator area, to accommodate events of today allowing sustainable development of the amphitheatre as well as the park and the district.
Under the Government's policy to improve the physical conditions of sub-standard school premises, ArchSD has carried out the construction of the new special school for children for the reprovisioning of The Church of Christ in China Mongkok Church Kai Oi School at a site near Hoi Lai Estate, Sham Shui Po. Located on an around 4,400 meter-square site, the newly built 4-storey building is equipped with multi-purpose facilities and designed to adopt extensive friendly and inclusive features for the special-needed students. For example, low-rise approach is adopted to ensure staff can maintain sight inspection of all students and easily accessible pocket spaces are available at different levels as calm-down spaces for students with special emotional needs.
The objective of this project is to design and construct a refuse collection point (RCP) for the Kai Tak Development in Kowloon, located on the eastern corner of an existing pumping station. The side was bound by Kai Tak Second Lane to the northeast and Shing Kai Road to the southeast. The project provides basic facilities like a refuse collection vehicle parking and loading area, a material recovery store, an office, staff toilets and changing rooms to accommodate the daily operations of a typical RCP.
Phase 1 of the redevelopment of Kwai Chung Hospital (KCH) comprises the construction of a decantation building and renovation works at existing premises of KCH for decanting purposes, so as to facilitate the next phases of the hospital redevelopment. The decantation building is a 5-storey building located at the existing car park area of Princess Margaret Hospital, accommodates facilities decanted from the existing KCH including rehabilitation facilities, ambulatory care facilities, administrative & supporting services, and other ancillary facilities.
In order to satisfy the growing demand of departmental quarters for married rank and file staff from the Immigrant Department, ArchSD commenced this project to construct a 15-storey quarters block for provision of a total of 112 units. With a total construction floor area of 8,800 meter square, the project comprises ancillary facilities including a management office, a multi-function room, small-scale outdoor children playing fixtures and facilities, 15 car parking spaces and two motorcycle parking spaces.
Building and sustainability, from sustainable development, energy saving, health and wellbeing are important considerations in the planning, construction, management, operation and maintenance of buildings. ArchSD and the Hong Kong Green Building Council have been working closely in developing and using building life cycle approach in the choice of green building materials and building design in minimising the emission of carbon. The department is also one of the pioneers in adopting the Building Environmental Assessment Method (BEAM) in the design, construction and maintenance of buildings.
ArchSD's representatives plays an active role in Green Building Council's committees, participating in discussions and providing expert advice on green building initiatives and the BEAM Plus rating system's certification and development. We are also pleased to see that the department has taken the initiative in adopting new technologies and innovative construction methods for new building developments, including the application of Modular Integrated Construction in a pilot project the Disciplined Services Quarters for the Fire Services Department at Pak Shing Kok, Tseung Kwan O.
We look forward to ArchSD's continuing effort to lead by example and to share experience with professionals in the building industry, and wish to express our appreciation of ArchSD's contributions.
Apart from new buildings, ArchSD has put great effort to improve the environmental performance of existing buildings through initiatives such as retrofitting and recommissioning. We devote ourselves to promote building sustainability in Hong Kong. We continue to practise sustainable building design and innovative construction methods in our projects. Moreover, we will collaborate with various professional bodies in organising regular briefings and sharing sessions on the latest trends of the building industry in order to raise public awareness and understanding.